Độ tinh khiết của một thành phần hoạt chất dược phẩm (API) phụ thuộc vào nhiều yếu tố như nguyên liệu thô, loại phản ứng, đường phản ứng và quá trình tinh lọc. Trong giai đoạn đầu của quá trình phát triển hóa học, điều cần thiết là phải đo và xác định sự hình thành tạp chất. Bằng cách lập biên dạng tạp chất, các nhà hóa học hữu cơ tổng hợp có thể thay đổi và kiểm soát các điều kiện phản ứng sao cho sự hình thành tạp chất có thể được giảm xuống mức có thể chấp nhận được, hoặc thậm chí tránh được. Đối với các cơ quan dược phẩm, lập biên dạng tạp chất là một dấu vân tay, cho thấy tin cậy của quá trình sản xuất. Do đó, lập biên dạng tạp chất tỉ mỉ chính xác và có thể tái là rất quan trọng cho bất kỳ ứng dụng thuốc mới nào.

Lập biên dạng tạp chất chính xác
Cùng với các mẫu phản ứng đại diện

Không bao giờ bỏ lỡ một mẫu
Thông tin phản hồi hoàn chỉnh
Các phản ứng hoá học lấy mẫu đáng tin cậy, bao gồm các hợp chất, các phản ứng ở áp suất cao, các phản ứng nhạy với không khí hoặc độ ẩm, và các phản ứng đa giai đoạn, thường khó khăn và tẻ nhạt. Ngoài ra, nhiều phản ứng rất lâu, hoặc có thể bắt đầu vào cuối ngày, gây khó khăn trong việc thu thập mẫu trong toàn bộ phản ứng. Do đó, có thể có một số mẫu thu thập được, và / hoặc lấy mẫu không thống nhất xảy ra khi phương pháp thu thập tốn nhiều thời gian hoặc khi lấy mẫu đại diện khó khăn. Trong khi đó, nếu các mẫu không được thu thập liên tục thì có thể tránh được mục tiêu chuyển đổi phản ứng, và mức tạp chất có thể đạt đến mức không mong muốn. Bằng cách sử dụng lấy mẫu tự động để liên tục thu thập các mẫu chính xác và có thể tái sản xuất để phân tích, các nhà hoá học sẽ thu được nhiều thông tin chất lượng hơn từ những thí nghiệm ít hơn, dẫn đến các quyết định nhanh chóng để phát triển hóa học sáng tạo.

Lập biên dạng tạp chất của
Phản ứng hữu cơ-kim loại nhạy không khí
Hai ghi chú ứng dụng thảo luận cách phản ứng mẫu của Janssen và Servier Pharmaceuticals không ảnh hưởng đến sự tiến triển của phản ứng:
- Lập biên dạng phản ứng của một hỗn hợp Buchwald-Hartwig Nhiệt độ cao
- Xác định điểm cuối của sự cắt giảm Ester nhạy không khí

Lấy mẫu phản ứng nhạy không khí
Động học phản ứng và phát hiện điểm cuối
Các phản ứng nhạy oxy rất khó khăn và tẻ nhạt để lấy mẫu, và thường đòi hỏi các thí nghiệm lặp lại để đạt được bộ dữ liệu hoàn chỉnh. Lấy mẫu thủ công đưa oxy vào bình phản ứng và ngăn chặn sự tiến triển của phản ứng. Hơn nữa, mẫu bị thay đổi khi chúng được đưa vào không khí trong quá trình lấy mẫu bằng tay. Những yếu tố này ảnh hưởng đến tốc độ phản ứng, tính chính xác và tính toàn vẹn của mẫu phản ứng và dẫn đến dữ liệu không đầy đủ và không nhất quán. Có khả năng nắm bắt được một mẫu đại diện từ các loại phản ứng một cách tự động cung cấp một bộ dữ liệu hoàn chỉnh và chính xác. Điều này cho phép nghiên cứu động học chính xác và tạo ra các biên dạng tạp chất đại diện để hiểu được tốc độ và cơ chế hình thành. Nói chung, các thí nghiệm giàu thông tin nâng cao năng suất và tiết kiệm chi phí, và dẫn đến thời gian phát triển giảm.
Lấy mẫu phản ứng hóa học
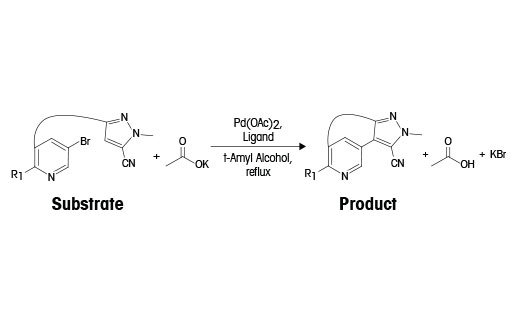
David Place, Pfizer, đã trình bày một nghiên cứu tình huống với phản ứng kích hoạt C-H được xúc tác palladium, thể hiện ở bên phải. Phản ứng nhạy oxy, và nồng độ oxy 5000 ppm trong không gian hơi sẽ làm tăng 50% thời gian phản ứng. Tuy nhiên, để phát triển phản ứng điều cần thiết là phải hiểu biên dạng động học, cơ chế tạo thành tạp chất, và chỉ định một điểm cuối hợp lý; nhưng việc lấy mẫu rất khó khăn khi không được đưa oxy vào phản ứng.
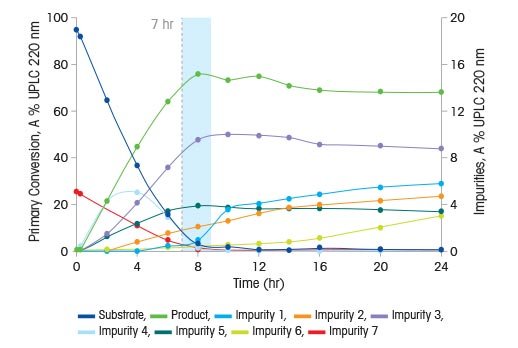
Lập biên dạng tạp chất với việc lấy mẫu tại chỗ
Đối với phản ứng này (cơ chế ở trên), mười hai mẫu được thu thập bằng cách sử dụng EasySampler lấy mẫu tại chỗ trong khoảng thời gian 24 giờ và được phân tích bằng UPLC (xem biểu đồ). Dữ liệu thu thập được trong suốt khoảng thời gian 24 giờ cung cấp cái nhìn sâu sắc về tính liên kết của các tạp chất được giám sát trong phản ứng, và đặc biệt nhấn mạnh sự cần thiết của chu kỳ thời gian phản ứng chặt chẽ. Các biên dạng chuyển đổi và tạp chất cho thấy khi sản phẩm đạt đến mức tối đa 8 giờ, hệ thống phản ứng phải được làm nguội ngay từ 102 ° C đến 20 ° C, để tránh sự hình thành Des-CN (tạp chất 1). Nếu hỗn hợp tiếp tục khuấy quá lâu, sản phẩm phụ sẽ hình thành đột ngột, và không thể dễ dàng bị loại bỏ trong các bước tiếp theo của quá trình xử lý và phản ứng. Dựa trên thông tin này, các nhà nghiên cứu nhanh chóng thiết lập các kiểm soát trong quá trình để tương quan thời gian phản ứng với mức tạp chất.

Tự động lấy mẫu để
Lập biên dạng tạp chất được cải thiện
Bài viết này xem xét 4 nghiên cứu tình huống từ Pfizer, trong đó lấy mẫu phản ứng hóa học tự động được áp dụng để thu thập các biên dạng tạp chất có thể tái sản xuất chất lượng cao trong hóa học mẫu khó (các chất dầy đặc, hỗn hợp ba pha, phản ứng nhạy oxy) bao gồm Ullman, Imidazolide, CH và Phản ứng Amin hóa.

Lấu mẫu tự động và không có giám sát
Mẫu sẵn sàng HPLC
EasySampler tự động cung cấp mẫu đại diện cho toàn bộ phản ứng. Các mẫu chính xác, có khả năng tái tạo và đại diện cho ra kết quả HPLC chất lượng cao. Điều này làm cho việc nghiên cứu động học phản ứng dễ dàng và phát triển cấu trúc tạp chất, ngay cả từ hỗn hợp không đồng nhất, phản ứng nhạy với không khí và độ ẩm, và phản ứng dưới điều kiện áp suất và điều kiện độc hại. Tại các điểm thời gian do người sử dụng xác định, EasySampler tự động chụp các mẫu phản ứng, làm dịu mẫu ngay lập tức và trong điều kiện phản ứng, và cuối cùng làm loãng mẫu đến nồng độ do người sử dụng chỉ định.

Công cụ Phát triển Hóa chất Đổi mới
Giải pháp tổng hợp và lấy mẫu tích hợp
Các thiết bị phản ứng tổng hợp tự động với lấy mẫu đại diện không có sự tham gia của con người thay đổi theo cách mà các nhà hóa học làm việc trong phòng thí nghiệm. Thiết lập là trực quan, và các thí nghiệm có thể bắt đầu bất cứ lúc nào và được an toàn để lại để tiến hành qua đêm. Với sự kiểm soát không cần có sự tham gia của con người và thu thập dữ liệu liên tục, các nhà khoa học có được lợi thế: hiểu, đổi mới và ra những quyết định sáng suốt.

Thư viện ứng dụng tổng hợp hữu cơ
- Trong động học
- Hóa học Isocyanate
- Hóa học Grignard
- Hydro hóa
- Tổng hợp Polyme
- Hoá học liên tục
Các Ứng dụng
Applications Related to Impurity Profiling of Chemical Reactions
Isocyanates are critical building blocks for high performance polyurethane-based polymers that make up coatings, foams, adhesives, elastomers, and insulation. Concerns over exposure to residual isocyanates led to new limits for residual isocyanates in new products. Traditional analytical methods for measuring the residual isocyanate (NCO) concentration using offline sampling and analysis raise concerns. In situ monitoring with process analytical technology addresses these challenges and enables manufacturers and formulators to ensure that product quality specifications, personnel safety, and environmental regulations are met.
Polymerization reaction measurement is crucial to produce material that meets requirements, including Immediate understanding, accurate and reproducible, Improved safety.
Kiến thức về động học tạp chất và cơ chế hình thành rất quan trọng trong việc xác định điểm cuối phản ứng trong các nghiên cứu phát triển hóa học và quá trình. Các mẫu phản ứng chính xác, tái sản xuất và đại diện là cần thiết cho các nghiên cứu này.
Theo dõi và Kiểm soát việc Tổng hợp Thuốc thử Grignard
Hydro hóa là một trong những phản ứng hóa học hàng đầu được sử dụng vì nó cho phép sự hình thành, trong một bước duy nhất, liên kết đơn C-C từ anken và alkynes, liên kết C-O từ xeton, aldehyt hoặc este và C-N (amin) từ imine hoặc nitrile.
Highly reactive chemistry is a terminology used to describe chemical reactions that are particularly challenging to handle and develop due to the potentially hazardous and/or energetic nature of the reactants, intermediates and products that are present during synthesis. These chemistries often involve highly exothermic reactions which require specialized equipment or extreme operating conditions (such as low temperature) to ensure adequate control. Ensuring safe operating conditions, minimizing human exposure, and gaining the maximum amount of information from each experiment are key factors in successfully designing and scaling-up highly reactive chemistries.
Nhiều quy trình yêu cầu phản ứng phải được diễn ra ở áp suất cao. Làm việc trong điều kiện áp suất thực sự là thách thức và lấy mẫu để đo offline là rất khó khăn và tốn thời gian. Sự thay đổi áp suất có thể ảnh hưởng đến tốc độ phản ứng, sự chuyển đổi và cơ chế cũng như các thông số khác của quá trình cộng với độ nhạy với oxy, nước và các vấn đề an toàn đều là những vấn đề thường gặp.
Halogenation occurs when one of more fluorine, chlorine, bromine, or iodine atoms replace one or more hydrogen atoms in an organic compound. Depending on the specific halogen, the nature of the substrate molecule and overall reaction conditions, halogenation reactions can be very energetic and follow different pathways. For this reason, understanding these reactions from a kinetics and thermodynamic perspective is critical to ensuring yield, quality and safety of the process.
Catalysts create an alternative path to increase the speed and outcome of a reaction, so a thorough understanding of the reaction kinetics is important. Not only does that provide information about the rate of the reaction, but also provides insight into the mechanism of the reaction. There are two types of catalytic reactions: heterogeneous and homogeneous. Heterogeneous is when the catalyst and reactant exist in two different phases. Homogeneous is when the catalyst and the reactant are in the same phase..
Phản ứng tổng hợp là một quá trình hóa học trong đó các nguyên tố hoặc hợp chất đơn giản kết hợp để tạo thành một sản phẩm phức tạp hơn. Nó được biểu diễn bằng phương trình: A + B → AB.
Design of Experiments (DoE) requires experiments to be conducted under well-controlled and reproducible conditions in chemical process optimization. Chemical synthesis reactors are designed to perform DoE investigations ensuring high quality data.
Reaction mechanisms describe the successive steps at the molecular level that take place in a chemical reaction. Reaction mechanisms cannot be proven, but rather postulated based on empirical experimentation and deduction. In situ FTIR spectroscopy provides information to support reaction mechanisms hypotheses.
Organometallic Synthesis, or Organometallic Chemistry, refers to the process of creating organometallic compounds, and is among the most researched areas in chemistry. Organometallic compounds are frequently used in fine chemical syntheses and to catalyze reactions. In situ Infrared and Raman spectroscopy are among the most powerful analytical methods for the study of organometallic compounds and syntheses.
Tổng hợp Oligonucleotide là quá trình hóa học trong đó các nucleotide được liên kết đặc biệt để tạo thành sản phẩm của trình tự mong muốn.
Alkylation is the process by when an alkyl group is added to a substrate molecule. Alkylation reactions are a widely used technique in organic chemistry.
Trang này trình bày khái niệm epoxit là gì, cách chúng được tổng hợp và công nghệ để theo dõi tiến trình phản ứng, bao gồm động học và các cơ chế chính.
The Suzuki and related cross-coupling reactions use transition metal catalysts, such as palladium complexes, to form C-C bonds between alkyl and aryl halides with various organic compounds.
Lithiation and organolithium reactions are key in the development of complex pharmaceutical compounds; organolithium compounds also act as initiators in certain polymerization reactions.
C-H bond activation is a series of mechanistic processes by which stable carbon-hydrogen bonds in organic compounds are cleaved.
Organocatalysis refers to the employment of particular organic molecules to speed up chemical reactions through catalytic activation.
Tổng hợp/ quá trình Hydroformyl hóa, hoặc oxo rất quan trọng trong việc sản xuất các olefin cho aldehyde và aldehyes từ alkenes. Các phản ứng hydroformyl hóa được thực hiện ở áp suất cao và có thể đặt ra thách thức đối với lấy mẫu do điều kiện phản ứng khắc nghiệt, cũng như các nguyên liệu thô và thuốc thử độc hại, dễ cháy, và dễ phản ứng.
Click reactions refer to chemical reactions that meet the criteria of click chemistry. Click reactions are typically fast, high-yielding, and occur under mild conditions, making them ideal for a variety of applications.
Lò phản ứng bể khuấy liên tục (CSTR) là một bình chứa thuốc thử và chất phản ứng chảy vào lò phản ứng, trong khi sản phẩm phản ứng thoát ra khỏi tàu.
Isocyanates are critical building blocks for high performance polyurethane-based polymers that make up coatings, foams, adhesives, elastomers, and insulation. Concerns over exposure to residual isocyanates led to new limits for residual isocyanates in new products. Traditional analytical methods for measuring the residual isocyanate (NCO) concentration using offline sampling and analysis raise concerns. In situ monitoring with process analytical technology addresses these challenges and enables manufacturers and formulators to ensure that product quality specifications, personnel safety, and environmental regulations are met.
Highly reactive chemistry is a terminology used to describe chemical reactions that are particularly challenging to handle and develop due to the potentially hazardous and/or energetic nature of the reactants, intermediates and products that are present during synthesis. These chemistries often involve highly exothermic reactions which require specialized equipment or extreme operating conditions (such as low temperature) to ensure adequate control. Ensuring safe operating conditions, minimizing human exposure, and gaining the maximum amount of information from each experiment are key factors in successfully designing and scaling-up highly reactive chemistries.
Nhiều quy trình yêu cầu phản ứng phải được diễn ra ở áp suất cao. Làm việc trong điều kiện áp suất thực sự là thách thức và lấy mẫu để đo offline là rất khó khăn và tốn thời gian. Sự thay đổi áp suất có thể ảnh hưởng đến tốc độ phản ứng, sự chuyển đổi và cơ chế cũng như các thông số khác của quá trình cộng với độ nhạy với oxy, nước và các vấn đề an toàn đều là những vấn đề thường gặp.
Halogenation occurs when one of more fluorine, chlorine, bromine, or iodine atoms replace one or more hydrogen atoms in an organic compound. Depending on the specific halogen, the nature of the substrate molecule and overall reaction conditions, halogenation reactions can be very energetic and follow different pathways. For this reason, understanding these reactions from a kinetics and thermodynamic perspective is critical to ensuring yield, quality and safety of the process.
Catalysts create an alternative path to increase the speed and outcome of a reaction, so a thorough understanding of the reaction kinetics is important. Not only does that provide information about the rate of the reaction, but also provides insight into the mechanism of the reaction. There are two types of catalytic reactions: heterogeneous and homogeneous. Heterogeneous is when the catalyst and reactant exist in two different phases. Homogeneous is when the catalyst and the reactant are in the same phase..
Reaction mechanisms describe the successive steps at the molecular level that take place in a chemical reaction. Reaction mechanisms cannot be proven, but rather postulated based on empirical experimentation and deduction. In situ FTIR spectroscopy provides information to support reaction mechanisms hypotheses.
Organometallic Synthesis, or Organometallic Chemistry, refers to the process of creating organometallic compounds, and is among the most researched areas in chemistry. Organometallic compounds are frequently used in fine chemical syntheses and to catalyze reactions. In situ Infrared and Raman spectroscopy are among the most powerful analytical methods for the study of organometallic compounds and syntheses.
Tổng hợp/ quá trình Hydroformyl hóa, hoặc oxo rất quan trọng trong việc sản xuất các olefin cho aldehyde và aldehyes từ alkenes. Các phản ứng hydroformyl hóa được thực hiện ở áp suất cao và có thể đặt ra thách thức đối với lấy mẫu do điều kiện phản ứng khắc nghiệt, cũng như các nguyên liệu thô và thuốc thử độc hại, dễ cháy, và dễ phản ứng.






















