Vägledning till kristallisationsutveckling
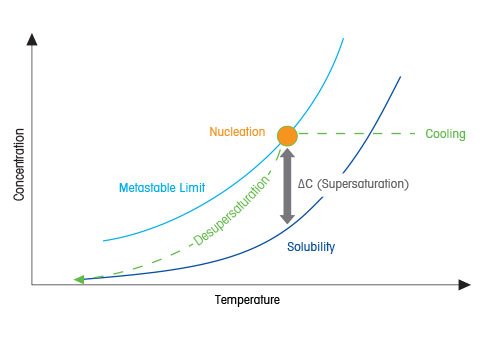
Definiera övermättnad
Drivkraften
Forskare får kontroll över kristallisationsprocesserna genom att omsorgsfullt justera övermättnadsnivån under processen. När en mättad lösning kyls ner, övergår systemet till ett metastabilt område där lösningen blir övermättad, eller med andra ord är mer löst ämne i lösningen än vad löslighetskurvan förutsäger. När kylningen fortsätter, kommer en viss temperatur att nås där kristallkärnbildningen inträffar, den metastabila gränsen.
Så snart som den metastabila gränsen har nåtts och kristallisationen inleds, förbrukas övermättnaden och så småningom kommer vätskefaskoncentrationen att nå jämvikt i löslighetskurvan.
Varför är övermättnad viktigt?
Eftersom övermättnad är drivkraften för kristallkärnbildning och tillväxt och är vad som i slutändan styr den slutgiltiga kristallstorleksfördelning, är det viktigt att förstå konceptet övermättnad.
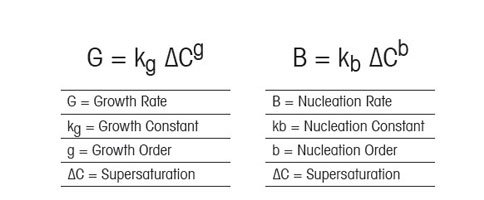
Kärnbildning är födseln av en ny kristallkärna – antingen spontant från lösning (primär kärnbildning) eller i närvaro av existerande kristaller (sekundär kärnbildning). Kristalltillväxten är ökningen i storlek (eller mera korrekt ”karakteristisk längd”) för kristallerna när löst ämne bildas från lösning. Relationen mellan övermättnad, kärnbildning och tillväxt definieras av en välkänd uppsättning (något förenklat) ekvationer som först förklarades av Nyvlt (Journal of Crystal Growth, Volym 3–4, 1968, sidorna 377–383)
Kristallkärnbildning och tillväxt
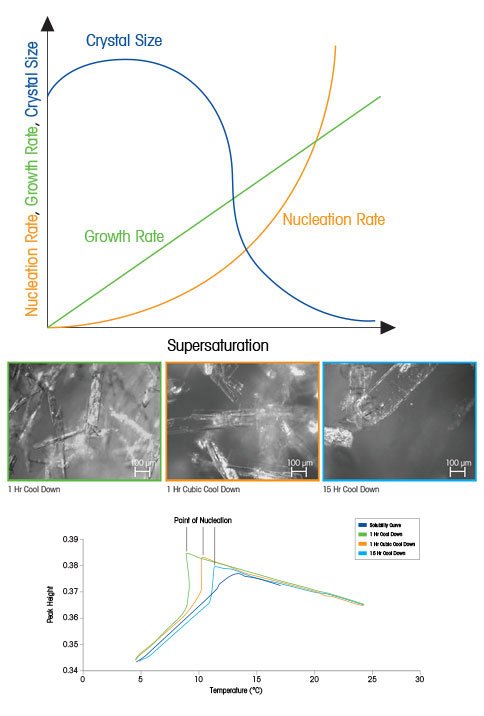
För organiska kristallisationssystem, är värdet för tillväxtordningen (g) vanligen mellan 1 och 2 och värdet för kärnbildningsordningen (b) är vanligen mellan 5 och 10. När man ställer upp dessa ekvationer för en teoretisk organisk kristallisationsprocess, blir betydelsen av övermättnad tydlig. Vid låg övermättnad, kan kristaller växa snabbare än de kan bilda kärnor, vilket leder till en större kristallstorleksfördelning. Vid högre övermättnad, dominerar dock kristallkärnbildningen kristalltillväxten, vilket i slutändan leder till mindre kristaller. I figuren till höger, där övermättnad presenteras i relation till kärnbildning, tillväxt och kristallstorlek, illustreras det tydligt hur kontroll av övermättnaden är av fundamental betydelse när det gäller att skapa kristaller med önskad storlek och fördelning.
Moderna tekniker som ReactIR, som här beskrivs av Barett, med flera (Chemical Engineering Research and Design, volym 88, nummer 8, augusti 2010, sidorna 1108–1119) gör det möjligt att utveckla löslighetsspår snabbt och enkelt och den rådande övermättnadsnivån som ska övervakas kontinuerligt under ett kristallisationsexperiment. Snabbare nedkylningshastigheter leder till kärnbildning vid lägre temperaturer och den högsta nivån av övermättnad under processen. En väldigt långsam nedkylning leder till en högre kärnbildningstemperatur och låg övermättnad under processen. En kubisk nedkylning på en timme (långsam i början och snabbare mot slutet) har genomgående en medelhög nivå av övermättnad. Påverkan av varierande övermättnad på kristallstorlek och formfördelning kan observeras tydligt genom att jämföra ParticleView (ett sondbaserat realtidsmikroskop)-bilder för varje experiment. Hög övermättnad leder till de minsta kristallerna – eftersom kärnbildning kommer att gynnas framför tillväxt.
Fallstudier om övermättnad och kontroll
Genom användning av experimentdata har mycket åstadkommits när det gäller övermättnadsövervakning och beräkning av kristallisationskinetik. Tillvägagångssättet har utvidgats till att möjliggöra modellbaserad kontroll av kristallisationsprocessen.

Teknologier för övervakning, optimering, kontroll
Användning av kristallisationsenheter erbjuder en unik möjlighet att rikta in sig på och kontrollera en optimerad kristallstorlek och formfördelning. Detta kan minska filtrerings- och torktiderna dramatiskt, undvika problem med förvaring, transport och hållbarhet och säkerställa en konsekvent och repeterbar process till lägre kostnad.

Hur man övervakar och kontrollerar övermättnad
Denna affisch beskriver användningen av en kalibreringsfri metod där temperaturen under nedkylningskristallisation kontrolleras automatiskt i ett vatten-/IPA-lösningsmedel för att upprätthålla en konstant övermättnadsnivå.

Optimera kristallisation med övermättnadskontroll
En metod presenteras som möjliggör kalibreringsfri användning av in situ ATR-FTIR-spektra för produktion och kontroll av kvalitativa övermättnadsbanor.

Vägledning till effektiv processutveckling
Denna white paper-serie täcker grundläggande och avancerade strategier för optimering av kristallstorlek och formfördelning.
Applikationer
Applications For The Driving Force For Crystal Nucleation and Growth
Recrystallization is a technique used to purify solid compounds by dissolving them in a hot solvent and allowing the solution to cool. During this process, the compound forms pure crystals as the solvent cools, while impurities are excluded. The crystals are then collected, washed, and dried, resulting in a purified solid product. Recrystallization is an essential method for achieving high levels of purity in solid compounds.
Det är vanligt att använda löslighetskurvor för att illustrera relationen mellan löslighet, temperatur och typ av lösningsmedel. Genom att kartlägga temperatur kontra löslighet, kan vetenskapsmän skapa det ramverk som krävs för att utveckla önskad kristallisationsprocess. Så snart som ett lämpligt lösningsmedel har valts, blir löslighetskurvan ett viktigt verktyg för utvecklingen av en effektiv kristallisationsprocess.
Forskare och tekniker får kontroll över kristallisationsprocesserna genom att omsorgsfullt justera övermättnadsnivån under processen. Övermättnad är drivkraften för kärnbildning och tillväxt under kristallisationen och styr den slutgiltiga kristallstorleksfördelningen.
Sondbaserade teknologier som används medan processen pågår tillämpas för att spåra storleks- och formförändringar för partiklar vid full koncentration utan behov av utspädning eller extraktion. Genom att spåra hastighet och förändringsgrad för partiklar och kristaller i realtid, kan de korrekta processparametrarna för kristallationsprestandan optimeras.
Seeding is one of the most critical steps in optimizing crystallization behavior. When designing a seeding strategy, parameters such as seed size, seed loading (mass), and seed addition temperature must be considered. These parameters are generally optimized based on process kinetics and the desired final particle properties, and must remain consistent during scale-up and technology transfer.
Liquid-Liquid phase separation, or oiling out, is an often difficult to detect particle mechanism that can occur during crystallization processes.
In an antisolvent crystallization, the solvent addition rate, addition location and mixing impact local supersaturation in a vessel or pipeline. Scientists and engineers modify crystal size and count by adjusting antisolvent addition protocol and the level of supersaturation.
Crystallization kinetics are characterized in terms of two dominant processes, nucleation kinetics and growth kinetics, occurring during crystallization from solution. Nucleation kinetics describe the rate of formation of a stable nuclei. Growth kinetics define the rate at which a stable nuclei grows to a macroscopic crystal. Advanced techniques offer temperature control to modify supersaturation and crystal size and shape.
Changing the scale or mixing conditions in a crystallizer can directly impact the kinetics of the crystallization process and the final crystal size. Heat and mass transfer effects are important to consider for cooling and antisolvent systems respectively, where temperature or concentration gradients can produce inhomogeneity in the prevailing level of supersaturation.
Crystal polymorphism describes the ability of one chemical compound to crystallize in multiple unit cell configurations, which often show different physical properties.
Protein crystallization is the act and method of creating structured, ordered lattices for often-complex macromolecules.
Lactose crystallization is an industrial practice to separate lactose from whey solutions via controlled crystallization.
A well-designed batch crystallization process is one that can be scaled successfully to production scale - giving the desired crystal size distribution, yield, form and purity. Batch crystallization optimization requires maintaining adequate control of the crystallizer temperature (or solvent composition).
Continuous crystallization is made possible by advances in process modeling and crystallizer design, which leverage the ability to control crystal size distribution in real time by directly monitoring the crystal population.
Recrystallization is a technique used to purify solid compounds by dissolving them in a hot solvent and allowing the solution to cool. During this process, the compound forms pure crystals as the solvent cools, while impurities are excluded. The crystals are then collected, washed, and dried, resulting in a purified solid product. Recrystallization is an essential method for achieving high levels of purity in solid compounds.
Det är vanligt att använda löslighetskurvor för att illustrera relationen mellan löslighet, temperatur och typ av lösningsmedel. Genom att kartlägga temperatur kontra löslighet, kan vetenskapsmän skapa det ramverk som krävs för att utveckla önskad kristallisationsprocess. Så snart som ett lämpligt lösningsmedel har valts, blir löslighetskurvan ett viktigt verktyg för utvecklingen av en effektiv kristallisationsprocess.
Sondbaserade teknologier som används medan processen pågår tillämpas för att spåra storleks- och formförändringar för partiklar vid full koncentration utan behov av utspädning eller extraktion. Genom att spåra hastighet och förändringsgrad för partiklar och kristaller i realtid, kan de korrekta processparametrarna för kristallationsprestandan optimeras.
Seeding is one of the most critical steps in optimizing crystallization behavior. When designing a seeding strategy, parameters such as seed size, seed loading (mass), and seed addition temperature must be considered. These parameters are generally optimized based on process kinetics and the desired final particle properties, and must remain consistent during scale-up and technology transfer.
Crystallization kinetics are characterized in terms of two dominant processes, nucleation kinetics and growth kinetics, occurring during crystallization from solution. Nucleation kinetics describe the rate of formation of a stable nuclei. Growth kinetics define the rate at which a stable nuclei grows to a macroscopic crystal. Advanced techniques offer temperature control to modify supersaturation and crystal size and shape.
Changing the scale or mixing conditions in a crystallizer can directly impact the kinetics of the crystallization process and the final crystal size. Heat and mass transfer effects are important to consider for cooling and antisolvent systems respectively, where temperature or concentration gradients can produce inhomogeneity in the prevailing level of supersaturation.
A well-designed batch crystallization process is one that can be scaled successfully to production scale - giving the desired crystal size distribution, yield, form and purity. Batch crystallization optimization requires maintaining adequate control of the crystallizer temperature (or solvent composition).
















