제품 브로슈어
Differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) is the most frequently used thermal analysis technique. DSC measures enthalpy changes in samples due to change...
Differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) is the most frequently used thermal analysis technique. DSC measures enthalpy changes in samples due to change...
Thermal Analysis comprises a group of techniques that measure the physical or chemical properties of a sample as a function of temperature or time whi...
Thermal analysis is a well-established analytical method that is widely used in many different fields. It provides laboratories with valuable results...
데이터 쉬트
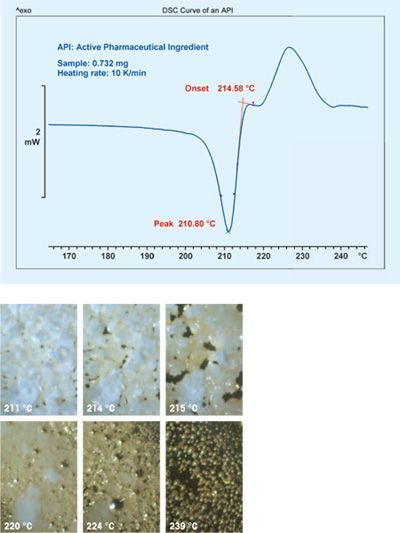
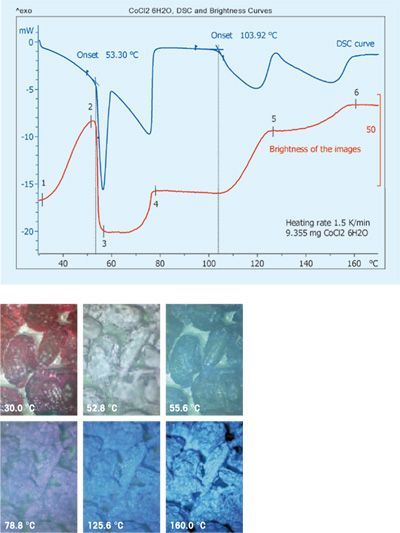
The system provides images of samples at predefined temperature or time intervals. A further evaluation possibility is to quantify color differences b...