Determination of Low Concentrations of Wax in Oils by DSC
The wax content (paraffin wax) in petroleum oils is an important parameter because critical physical properties of the oil such as the viscosity change with the wax content. Furthermore, the wax present in an oil may solidify and precipitate out at low temperatures. Determination of the wax content is therefore an important analytical requirement in quality control.
Figure 1. Measurement curves of an oil using two different crucibles ( red: 7.0 mg in a 40- μL standard aluminum crucible, black: 49.5 mg in a 100-μL aluminum crucible ).
Introduction
The wax most often present in petroleum oil is paraffin wax (CnH2n+2) with a chain length of about 18 to 36 carbon atoms. These substances melt above room temperature between 45 and 65 ° C.
Different methods are available for determining the wax content in oils, for example:
- Extraction of the wax
- Determination of the pour point of the oil
- Determination of the cloud point of the oil
- Optical measurements using polarization microscopy
- NMR
These methods all have various disadvantages such as long analysis time, the use of chemicals, large sample amounts or relatively poor detection limits.
DSC can be used to measure the melting behavior of the wax. The analysis of the wax peak in the DSC curve is a simple method that requires only a small amount of sample. Systematic studies of oils with different waxes can be found in the scientific literature [1, 2].
These publications describe methods in which liquid waxes are measured at lower temperatures and solid waxes such as paraffin wax are measured at temperatures above room temperature.
Experimental Details
All measurements were performed in the temperature range 10 to 80 ° C at a heating rate of 10 K / min using a METTLER TOLEDO DSC 1 equipped with an IntraCooler. Both 40-μL standard aluminum crucibles and 100-μL aluminum crucibles were used...
Download the full text of this article below.
Conclusions
The wax content in different oils can be quickly and easily determined by DSC if the right experimental conditions are used. In this method, it is important to use large crucibles in order to reliably measure the melting peak of waxes in oils with low wax contents.
Determination of Low Concentrations of Wax in Oils by DSC | Thermal Analysis Application No. UC386 | Application published in METTLER TOLEDO Thermal Analysis UserCom 38
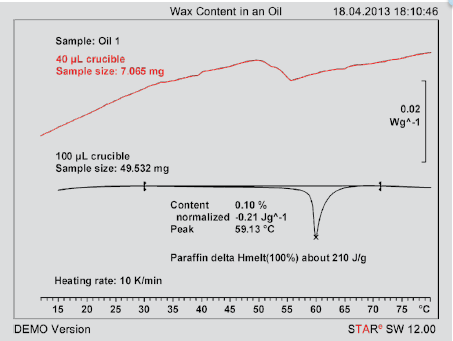 Figure 1. Measurement curves of an oil using two different crucibles ( red : 7.0 mg in a 40- μL standard aluminum crucible, black : 49.5 mg in a 100-μL aluminum crucible ).
Figure 1. Measurement curves of an oil using two different crucibles ( red : 7.0 mg in a 40- μL standard aluminum crucible, black : 49.5 mg in a 100-μL aluminum crucible ).The wax content (paraffin wax) in petroleum oils is an important parameter because critical physical properties of the oil such as the viscosity change with the wax content. Furthermore, the wax present in an oil may solidify and precipitate out at low temperatures. Determination of the wax content is therefore an important analytical requirement in quality control.
Introduction
The wax most often present in petroleum oil is paraffin wax (CnH2n+2) with a chain length of about 18 to 36 carbon atoms. These substances melt above room temperature between 45 and 65 ° C.
Different methods are available for determining the wax content in oils, for example:
- Extraction of the wax
- Determination of the pour point of the oil
- Determination of the cloud point of the oil
- Optical measurements using polarization microscopy
- NMR
These methods all have various disadvantages such as long analysis time, the use of chemicals, large sample amounts or relatively poor detection limits.
DSC can be used to measure the melting behavior of the wax. The analysis of the wax peak in the DSC curve is a simple method that requires only a small amount of sample. Systematic studies of oils with different waxes can be found in the scientific literature [1, 2].
These publications describe methods in which liquid waxes are measured at lower temperatures and solid waxes such as paraffin wax are measured at temperatures above room temperature.
Experimental details
All measurements were performed in the temperature range 10 to 80 ° C at a heating rate of 10 K / min using a METTLER TOLEDO DSC 1 equipped with an IntraCooler. Both 40-μL standard aluminum crucibles and 100-μL aluminum crucibles were used...
Download the full text of this article below.
Conclusions
The wax content in different oils can be quickly and easily determined by DSC if the right experimental conditions are used. In this method, it is important to use large crucibles in order to reliably measure the melting peak of waxes in oils with low wax contents.
Determination of Low Concentrations of Wax in Oils by DSC | Thermal Analysis Application No. UC386 | Application published in METTLER TOLEDO Thermal Analysis UserCom 38