
pH Electrolytes and Maintenance Solutions
Quality Solutions to Store and Maintain Your Sensor
pH electrolytes and maintenance solutions are standards that ensure the sensor is protected and measures accurately. The sensor is the main actor of the measurement, requiring, therefore, special care and attention. METTLER TOLEDO offers the necessary pH maintenance and storage solutions along with quality electrolytes to ensure the sensor is ready to measure and provides accurate readings. Offered in a variety of sizes, choose between 25 mL or 250 mL single- or six-pack options.
Advantages of METTLER TOLEDO's pH Electrolytes and Maintenance Solutions
Find the Right Electrolyte
The correct pH electrolyte will minimize potential junction errors and provide optimum temperature and time responses. The proper electrolyte to use is written on the sensor shaft. The pH electrolyte must be refilled or replaced regularly to achieve good electrode performance. Our pH sensors come with a special wetting cap that makes refilling easy.

Store the Sensor in a Proper Solution
Electrodes should always be stored in aqueous and ion-rich solutions. The InLab® storage solution provides optimal conditions for sensors during the time between measurements, be it short- or long-term storage.

Keep the Sensor Cleaned
Using a dirty electrode is one of the typical sources of error in pH measurement. Whenever rinsing with deionized water is not sufficient, a special cleaning solution can be used to remove sample residues. Depending on the contamination, Pepsin-HCl or Thiourea is recommended.
Download Your Certificate
To guarantee maximum traceability, an individual test certificate exists for every batch of pH maintenance or storage solution. The pH sensor maintenance or storage solution certificate can easily be downloaded and printed for documentation purposes. Read more
Get a Safety Datasheet
Remaining compliant with regulations is important. All SDS (Safety Data Sheet) documents and labels contain information on your pH storage or maintenance solution according to the GHS (Global Harmonized System) in local languages. Read more
Minimize Contamination Risk
For high accuracy, uncontaminated solutions are of utmost importance. For pH electrolyte solutions, we offer 25 or 250 mL single- or six-pack options. pH maintenance solutions are also offered in small bottles, enabling easy handling and reducing the contamination risk.
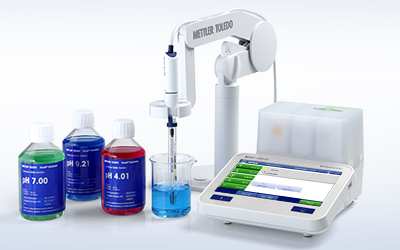
All-In-One Solution
METTLER TOLEDO provides entire electrochemistry systems—from meters and sensors to calibration solutions and software. Benefit from a broad portfolio, choose the right sensor for your application, and maintain and store it correctly with the proper pH electrolytes and maintenance solutions.
Explore Our Services - Tailored to Fit Your Equipment
We support and service your measurement equipment through its entire life-cycle, from installation to preventive maintenance and calibration to equipment repair.
Support & Repair

FAQs
What is a pH reference electrolyte?
The reference electrolyte ensures a stable signal transmission. Due to its high ion concentration, the reference electrolyte conducts the electronic signal from the reference element (mainly Ag/AgCl) to the measured medium. It thus closes the electronic circuit of the pH measurement system.
What is the difference between refillable liquid and gel electrolytes?
Electrodes with refillable liquid reference electrolyte will have a longer life, less risk of reference contamination, and faster response time than electrodes with gel electrolyte. However, sensors with gel electrolyte are easier to maintain.
How should I store my sensor?
pH glass sensors need to be kept moist at all times. If an electrode dries out during storage, a regeneration procedure is required to restore the hydrated glass layer and the reference junction in order to make the sensor operable. As a general rule, store your pH sensor in the same solution as the reference electrolyte of the sensor. In most cases, InLab® Storage solution can be used. Sensors with a bridge electrolyte should be stored in the electrolyte of the outer electrolyte compartment.
How should I clean my pH sensor?
Your pH sensor should be cleaned regularly. Reduced slope and/or offset or slow response time are an indication that your sensor needs cleaning. Fats, oils, and grease should be cleaned with a non-ionic surfactant solution or methanol. Proteins should be cleaned with a Pepsin-HCl Cleaner solution. After cleaning, rinse the sensor with deionized water, recondition it in 3M KCl and then store it in store in the InLab® Storage Solution.
What is the expected outflow of the reference pH electrolyte?
- 1 mL per 24 hours for electrodes with a ceramic diaphragm (e.g., InLab® Routine)
- 3 mL per 24 hours for electrodes with a sleeve diaphragm (e.g., InLab Science)
- Electrodes with a solid-state electrolyte and open junction (e.g., InLab Expert) have no outflow but only "exchange" of ions via diffusion
Does the inner pH electrolyte level in a bridge electrode need to be greater than the outer pH electrolyte?
Yes. If the bridge electrolyte has a higher filling level, then it flows into the chamber with the pH reference electrolyte (due to the higher pressure at the inner junction). This changes the composition and is not pure 3 mol/L KCl anymore. The reference signal of the electrode depends on the solution's composition, hence, the measured potential between measuring half-cell and reference half-cell changes due to it.
Is crystallization of the electrolyte and salt deposits dangerous?
Salt buildup and crystallization of KCL are not harmful to the electrode and do not inhibit its performance. However, it should be removed before measurement.










