Produkt-Broschüren
Die dynamische Differenzkalorimetrie (DDK, englisch DSC) ist die am häufigsten verwendete thermische Analysetechnik. Sie misst Enthalpieänderungen in...
Die dynamische Differenzkalorimetrie (DDK, englisch DSC) ist die am häufigsten verwendete thermische Analysetechnik. Sie misst Enthalpieänderungen in...
Die Excellence-Linie für die thermische Analyse von METTLER TOLEDO bietet Ihnen massgeschneiderte Lösungen für verschiedene akademische und industriel...
Die thermische Analyse ist mittlerweile in vielen Bereichen eine fest etablierte Analysenmethode. Ob in der Qualitätssicherung und -kontrolle, der Pr...
Datenblätter
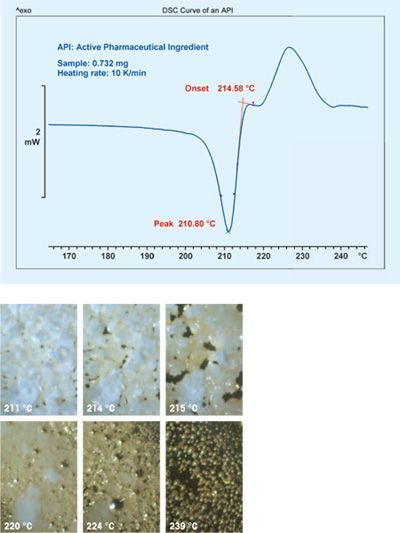
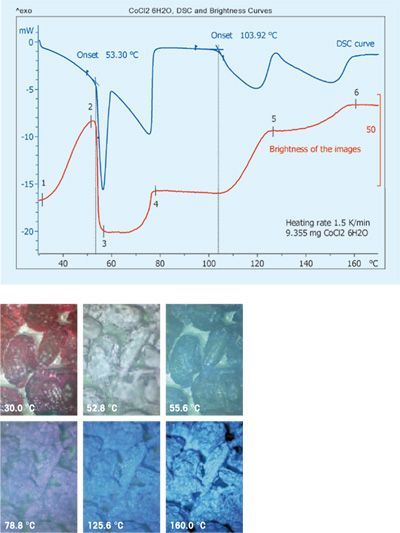
The system provides images of samples at predefined temperature or time intervals. A further evaluation possibility is to quantify color differences b...